Riemannian manifold
In differential geometry, a Riemannian manifold (or Riemannian space) , so called after the German mathematician Bernhard Riemann, is a real, smooth manifold equipped with a smoothly-varying family of positive-definite inner products on the tangent spaces at each point .[1]
The family of inner products is called a Riemannian metric (or a Riemannian metric tensor, or just a metric).[1] It is a special case of a metric tensor. Riemannian geometry is the study of Riemannian manifolds.
A Riemannian metric makes it possible to define many geometric notions, including angles, lengths of curves, areas of surfaces, higher-dimensional analogues of area (volumes, etc.), extrinsic curvature of submanifolds, and the intrinsic curvature of the manifold itself.
The requirement that is smoothly-varying amounts to that for any smooth coordinate chart on , the functions
are smooth functions, i.e., they are infinitely differentiable.[1]
History

In 1827, Carl Friedrich Gauss discovered that the Gaussian curvature of a surface embedded in 3-dimensional space only depends on local measurements made within the surface (the first fundamental form).[2] This result is known as the Theorema Egregium ("remarkable theorem" in Latin).
A map that preserves the local measurements of a surface is called a local isometry. Call a property of a surface an intrinsic property if it is preserved by local isometries and call it an extrinsic property if it is not. In this language, the Theorema Egregium says that the Gaussian curvature is an intrinsic property of surfaces.
Riemannian manifolds and their curvature were first introduced non-rigorously by Bernhard Riemann in 1854.[3] However, they would not be formalized until much later. In fact, the more primitive concept of a smooth manifold was first explicitly defined only in 1913 in a book by Hermann Weyl.[3]
Élie Cartan introduced the Cartan connection, one of the first concepts of a connection. Levi-Civita defined the Levi-Civita connection, a special connection on a Riemannian manifold.
Albert Einstein used the theory of pseudo-Riemannian manifolds (a generalization of Riemannian manifolds) to develop general relativity. In particular, his equations for gravitation are constraints on the curvature of spacetime. Other applications of Riemannian geometry include computer graphics and artificial intelligence.
Definition
Riemannian metrics and Riemannian manifolds

Let be a smooth manifold. For each point , there is an associated vector space called the tangent space of at . Vectors in are thought of as the vectors tangent to at .
However, does not come equipped with an inner product, a measuring stick that gives tangent vectors a concept of length and angle. This is an important deficiency because calculus teaches that to calculate the length of a curve, the length of vectors tangent to the curve must be defined. A Riemannian metric puts a measuring stick on every tangent space.
A Riemannian metric on assigns to each a positive-definite inner product in a smooth way (see the section on regularity below).[1] This induces a norm defined by . A smooth manifold endowed with a Riemannian metric is a Riemannian manifold, denoted .[1] A Riemannian metric is a special case of a metric tensor.
The Riemannian metric in coordinates
If are smooth local coordinates on , the vectors
form a basis of the vector space for any . Relative to this basis, one can define the Riemannian metric's components at each point by
- .[4]
These functions can be put together into an matrix-valued function on . The requirement that is a positive-definite inner product then says exactly that this matrix-valued function is a symmetric positive-definite matrix at .
In terms of the tensor algebra, the Riemannian metric can be written in terms of the dual basis of the cotangent bundle as
Regularity of the Riemannian metric
The Riemannian metric is continuous if its components are continuous in any smooth coordinate chart The Riemannian metric is smooth if its components are smooth in any smooth coordinate chart. One can consider many other types of Riemannian metrics in this spirit, such as Lipschitz Riemannian metrics or measurable Riemannian metrics.
There are situations in geometric analysis in which one wants to consider non-smooth Riemannian metrics. See for instance (Gromov 1999) and (Shi and Tam 2002). The section Riemannian manifolds with continuous metrics handles the case where is merely continuous, but is assumed to be smooth in this article unless stated otherwise.
Musical isomorphism
In analogy to how an inner product on a vector space induces an isomorphism between a vector space and its dual given by , a Riemannian metric induces an isomorphism of bundles between the tangent bundle and the cotangent bundle. Namely, if is a Riemannian metric, then
is a bundle isomorphism from the tangent bundle to the cotangent bundle .[5]
Isometries
An isometry is a function between Riemannian manifolds which preserves all of the structure of Riemannian manifolds. If two Riemannian manifolds have an isometry between them, they are called isometric, and they are considered to be the same manifold for the purpose of Riemannian geometry.
Specifically, if and are two Riemannian manifolds, a diffeomorphism is called an isometry if ,[6] that is, if
for all and For example, translations and rotations are both isometries from Euclidean space (to be defined soon) to itself.
One says that a smooth map not assumed to be a diffeomorphism, is a local isometry if every has an open neighborhood such that is an isometry (and thus a diffeomorphism).[6]
Volume
An oriented -dimensional Riemannian manifold has a unique -form called the Riemannian volume form.[7] The Riemannian volume form is preserved by orientation-preserving isometries.[8] The volume form gives rise to a measure on which allows measurable functions to be integrated.[citation needed] If is compact, the volume of is .[7]
Examples
Euclidean space
Let denote the standard coordinates on The (canonical) Euclidean metric is given by[9]
or equivalently
or equivalently by its coordinate functions
- where is the Kronecker delta.
The Riemannian manifold is called Euclidean space.
Submanifolds

Let be a Riemannian manifold and let be an immersed submanifold or an embedded submanifold of . The pullback of is a Riemannian metric on , and is said to be a Riemannian submanifold of .[10]
In the case where , the map is given by and the metric is just the restriction of to vectors tangent along . In general, the formula for is
where is the pushforward of by
Examples:
- The -sphere
- is a smooth embedded submanifold of Euclidean space .[11] The Riemannian metric this induces on is called the round metric or standard metric.
- Fix real numbers . The ellipsoid
- is a smooth embedded submanifold of Euclidean space .
- The graph of a smooth function is a smooth embedded submanifold of with its standard metric.
- If is not simply connected, there is a covering map , where is the universal cover of . This is an immersion (since it is locally a diffeomorphism), so automatically inherits a Riemannian metric. By the same principle, any smooth covering space of a Riemannian manifold inherits a Riemannian metric.
On the other hand, if already has a Riemannian metric , then the immersion (or embedding) is called an isometric immersion (or isometric embedding) if . Hence isometric immersions and isometric embeddings are Riemannian submanifolds.[10]
Products
Let and be two Riemannian manifolds, and consider the product manifold . The Riemannian metrics and naturally put a Riemannian metric on which can be described in a few ways.
- Considering the decomposition one may define
- If is a smooth coordinate chart on and is a smooth coordinate chart on , then is a smooth coordinate chart on Let be the representation of in the chart and let be the representation of in the chart . The representation of in the coordinates is
- where [12]
For example, consider the -torus . If each copy of is given the round metric, the product Riemannian manifold is called the flat torus.
Positive combinations of metrics
Let be Riemannian metrics on If are any positive numbers, then is another Riemannian metric on
Every smooth manifold admits a Riemannian metric
Theorem: Every smooth manifold admits a (non-canonical) Riemannian metric.[13]
This is a fundamental result. Although much of the basic theory of Riemannian metrics can be developed using only that a smooth manifold is a locally Euclidean topological space, for this result it is necessary to use that smooth manifolds are Hausdorff and paracompact. The reason is that the proof makes use of a partition of unity.
Proof that every smooth manifold admits a Riemannian metric |
|---|
| Let be a smooth manifold and a locally finite atlas so that are open subsets and are diffeomorphisms. Such an atlas exists because the manifold is paracompact. Let be a differentiable partition of unity subordinate to the given atlas, i.e. such that for all . Define a Riemannian metric on by where Here is the Euclidean metric on and is its pullback along . While is only defined on , the product is defined and smooth on since . It takes the value 0 outside of . Because the atlas is locally finite, at every point the sum contains only finitely many nonzero terms, so the sum converges. Now one needs to check that is actually a Riemannian metric. That is, one needs to check that is smooth at and that for fixed it is positive-definite, symmetric, and linear in the first argument. Symmetry is verified as follows: Linearity in the first argument is verified as follows: Positive-definiteness is verified as follows: Because the atlas is locally finite, has a neighborhood on which the sum contains only finitely many nonzero terms. On this neighborhood, is a finite sum of smooth functions. Therefore is smooth at . |
An alternative proof uses the Whitney embedding theorem to embed into Euclidean space and then pulls back the metric from Euclidean space to . On the other hand, the Nash embedding theorem states that, given any smooth Riemannian manifold there is an embedding for some such that the pullback by of the standard Riemannian metric on is That is, the entire structure of a smooth Riemannian manifold can be encoded by a diffeomorphism to a certain embedded submanifold of some Euclidean space. Therefore, one could argue that nothing can be gained from the consideration of abstract smooth manifolds and their Riemannian metrics. However, there are many natural smooth Riemannian manifolds, such as the set of rotations of three-dimensional space and the hyperbolic space, of which any representation as a submanifold of Euclidean space will fail to represent their remarkable symmetries and properties as clearly as their abstract presentations do.
Metric space structure
An admissible curve is a piecewise smooth curve whose velocity is nonzero everywhere it is defined. The nonnegative function is defined on the interval except for at finitely many points. The length of an admissible curve is defined as
The integrand is bounded and continuous except at finitely many points, so it is integrable. For a connected Riemannian manifold, define by
Theorem: is a metric space, and the metric topology on coincides with the topology on .[14]
Proof sketch that is a metric space, and the metric topology on agrees with the topology on |
|---|
| In verifying that satisfies all of the axioms of a metric space, the most difficult part is checking that implies . Verification of the other metric space axioms is omitted. There must be some precompact open set around p which every curve from p to q must escape. By selecting this open set to be contained in a coordinate chart, one can reduce the claim to the well-known fact that, in Euclidean geometry, the shortest curve between two points is a line. In particular, as seen by the Euclidean geometry of a coordinate chart around p, any curve from p to q must first pass though a certain "inner radius." The assumed continuity of the Riemannian metric g only allows this "coordinate chart geometry" to distort the "true geometry" by some bounded factor. To be precise, let be a smooth coordinate chart with and Let be an open subset of with By continuity of and compactness of there is a positive number such that for any and any where denotes the Euclidean norm induced by the local coordinates. Let R denote to be used at the final step of the proof. Now, given any admissible curve from p to q, there must be some minimal such that clearly The length of is at least as large as the restriction of to So The integral which appears here represents the Euclidean length of a curve from 0 to , and so it is greater than or equal to R. So we conclude The observation about comparison between lengths measured by g and Euclidean lengths measured in a smooth coordinate chart, also verifies that the metric space topology of coincides with the original topological space structure of . |
Although the length of a curve is given by an explicit formula, it is generally impossible to write out the distance function by any explicit means. In fact, if is compact, there always exist points where is non-differentiable, and it can be remarkably difficult to even determine the location or nature of these points, even in seemingly simple cases such as when is an ellipsoid.[citation needed]
Diameter
The diameter of the metric space is
The Hopf–Rinow theorem shows that if is complete and has finite diameter, it is compact. Conversely, if is compact, then the function has a maximum, since it is a continuous function on a compact metric space. This proves the following.
- If is complete, then it is compact if and only if it has finite diameter.
This is not the case without the completeness assumption; for counterexamples one could consider any open bounded subset of a Euclidean space with the standard Riemannian metric. It is also not true that any complete metric space of finite diameter must be compact; it matters that the metric space came from a Riemannian manifold.
Connections, geodesics, and curvature
Connections
An (affine) connection is an additional structure on a Riemannian manifold that defines differentiation of one vector field with respect to another. Connections contain geometric data, and two Riemannian manifolds with different connections have different geometry.
Let denote the space of vector fields on . An (affine) connection
on is a bilinear map such that
- For every function ,
- The product rule holds.[15]
The expression is called the covariant derivative of with respect to .
Levi-Civita connection
Two Riemannian manifolds with different connections have different geometry. Thankfully, there is a natural connection associated to a Riemannian manifold called the Levi-Civita connection.
A connection is said to preserve the metric if
A connection is torsion-free if
where is the Lie bracket.
A Levi-Civita connection is a torsion-free connection that preserves the metric. Once a Riemannian metric is fixed, there exists a unique Levi-Civita connection.[16]
Covariant derivative along a curve
If is a smooth curve, a smooth vector field along is a smooth map such that for all . The set of smooth vector fields along is a vector space under pointwise vector addition and scalar multiplication.[17] One can also pointwise multiply a smooth vector field along by a smooth function :
- for
Let be a smooth vector field along . If is a smooth vector field on a neighborhood of the image of such that , then is called an extension of .
Given a fixed connection on and a smooth curve , there is a unique operator , called the covariant derivative along , such that:[18]
- If is an extension of , then .
Geodesics


Geodesics are curves with no intrinsic acceleration. They are the generalization of straight lines in Euclidean space to arbitrary Riemannian manifolds. An ant living in a Riemannian manifold walking straight ahead without making any effort to accelerate or turn would trace out a geodesic.
Fix a connection on . Let be a smooth curve. The acceleration of is the vector field along . If for all , is called a geodesic.[19]
For every and , there exists a geodesic defined on some open interval containing 0 such that and . Any two such geodesics agree on their common domain.[20] Taking the union over all open intervals containing 0 on which a geodesic satisfying and exists, one obtains a geodesic called a maximal geodesic of which every geodesic satisfying and is a restriction.[21]
Every curve that has the shortest length of any admissible curve with the same endpoints as is a geodesic (in a unit-speed reparameterization).[22]
Examples
- The nonconstant maximal geodesics of the Euclidean plane are exactly the straight lines.[21] This agrees the fact from Euclidean geometry that the shortest path between two points is a straight line segment.
- The nonconstant maximal geodesics of with the round metric are exactly the great circles.[23] Since the Earth is approximately a sphere, this means that the shortest path a plane can fly between two locations on Earth is a segment of a great circle.
Hopf–Rinow theorem

The Riemannian manifold with its Levi-Civita connection is geodesically complete if the domain of every maximal geodesic is .[24]. The plane is geodesically complete. On the other hand, the punctured plane with the restriction of the Riemannian metric from is not geodesically complete as the maximal geodesic with initial conditions , does not have domain .
The Hopf–Rinow theorem characterizes geodesically complete manifolds.
Theorem: Let be a connected Riemannian manifold. The following are equivalent:[25]
- The metric space is complete (every -Cauchy sequence converges),
- All closed and bounded subsets of are compact,
- is geodesically complete.
Parallel transport
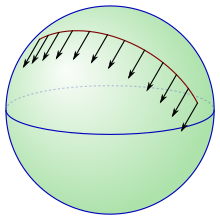
In Euclidean space, all tangent spaces are canonically identified with each other via translation, so it is easy to move vectors from one tangent space to another. Parallel transport is a way of moving vectors from one tangent space to another along a curve in the setting of a general Riemannian manifold. Given a fixed connection, there is a unique way to do parallel transport.[26]
Specifically, call a smooth vector field along a smooth curve parallel along if identically.[21] Fix a curve with and . to parallel transport a vector to a vector in along , first extend to a vector field parallel along , and then take the value of this vector field at .
The images below show parallel transport induced by the Levi-Civita connection associated to two different Riemannian metrics on the punctured plane . The curve the parallel transport is done along is the unit circle. In polar coordinates, the metric on the left is the standard Euclidean metric , while the metric on the right is . This second metric has a singularity at the origin, so it does not extend past the puncture, but the first metric extends to the entire plane.


Warning: This is parallel transport on the punctured plane along the unit circle, not parallel transport on the unit circle. Indeed, in the first image, the vectors fall outside of the tangent space to the unit circle.
Riemann curvature tensor
The Riemann curvature tensor measures precisely the extent to which parallel transporting vectors around a small rectangle is not the identity map.[27] The Riemann curvature tensor is 0 at every point if and only if the manifold is locally isometric to Euclidean space.[28]
Fix a connection on . The Riemann curvature tensor is the map defined by
where is the Lie bracket of vector fields. The Riemann curvature tensor is a -tensor field.[29]
Ricci curvature tensor
The Ricci curvature tensor plays a defining role in the theory of Einstein manifolds. Specifically, a (pseudo-)Riemannian metric is called an Einstein metric if Einstein's equation
- for some constant
holds.[30]
Fix a connection on . The Ricci curvature tensor is
where is the trace. The Ricci curvature tensor is a covariant 2-tensor field.[31]
Scalar curvature
Riemannian manifolds with continuous metrics
Throughout this section, Riemannian metrics will be assumed to be continuous but not necessarily smooth.
- Isometries between Riemannian manifolds with continuous metrics are defined the same as in the smooth case.
- One can consider Riemannian submanifolds of Riemannian manifolds with continuous metrics. The pullback metric of a continuous metric through a smooth function is still a continuous metric.
- The product of Riemannian manifolds with continuous metrics is defined the same as in the smooth case and yields a Riemannian manifold with a continuous metric.
- The positive combination of continuous Riemannian metrics is a continuous Riemannian metric.
- The length of an admissible curve is defined exactly the same as in the case when the metric is smooth.[32]
- The Riemannian distance function is defined exactly the same as in the case when the metric is smooth. As before, is a metric space, and the metric topology on coincides with the topology on .[33]
Infinite-dimensional manifolds
The statements and theorems above are for finite-dimensional manifolds—manifolds whose charts map to open subsets of These can be extended, to a certain degree, to infinite-dimensional manifolds; that is, manifolds that are modeled after a topological vector space; for example, Fréchet, Banach, and Hilbert manifolds.
Definitions
Riemannian metrics are defined in a way similar to the finite-dimensional case. However, there is a distinction between two types of Riemannian metrics:
- A weak Riemannian metric on is a smooth function such that for any the restriction is an inner product on [citation needed]
- A strong Riemannian metric on is a weak Riemannian metric such that induces the topology on . If is a strong Riemannian metric, then must be a Hilbert manifold.[citation needed]
Examples
- If is a Hilbert space, then for any one can identify with The metric for all is a strong Riemannian metric.[citation needed]
- Let be a compact Riemannian manifold and denote by its diffeomorphism group. The latter is a smooth manifold (see here) and in fact, a Lie group.[citation needed] Its tangent bundle at the identity is the set of smooth vector fields on [citation needed] Let be a volume form on The weak Riemannian metric on , denoted , is defined as follows. Let Then for ,
- .[citation needed]
Metric space structure
Length of curves and the Riemannian distance function are defined in a way similar to the finite-dimensional case. The distance function , called the geodesic distance, is always a pseudometric (a metric that does not separate points), but it may not be a metric.[34] In the finite-dimensional case, the proof that the Riemannian distance function separates points uses the existence of a pre-compact open set around any point. In the infinite case, open sets are no longer pre-compact, so the proof fails.
- If is a strong Riemannian metric on , then separates points (hence is a metric) and induces the original topology.[citation needed]
- If is a weak Riemannian metric, may fail to separate points. In fact, it may even be identically 0.[34] For example, if is a compact Riemannian manifold, then the weak Riemannian metric on induces vanishing geodesic distance.[35]
Hopf–Rinow theorem
In the case of strong Riemannian metrics, one part of the finite-dimensional Hopf–Rinow still holds.
Theorem: Let be a strong Riemannian manifold. Then metric completeness (in the metric ) implies geodesic completeness.[citation needed]
However, a geodesically complete strong Riemannian manifold might not be metrically complete and it might have closed and bounded subsets that are not compact.[citation needed] Further, a strong Riemannian manifold for which all closed and bounded subsets are compact might not be geodesically complete.[citation needed]
If is a weak Riemannian metric, then no notion of completeness implies the other in general.[citation needed]
See also
References
Notes
- ^ a b c d e do Carmo 1992, p. 38.
- ^ do Carmo 1992, pp. 35–36.
- ^ a b do Carmo 1992, p. 37.
- ^ a b Lee 2018, p. 13.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 26.
- ^ a b Lee 2018, p. 12.
- ^ a b Lee 2018, p. 30.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 31.
- ^ Lee 2018, pp. 12–13.
- ^ a b Lee 2018, p. 15.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 16.
- ^ a b Lee 2018, p. 20.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 11.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 39.
- ^ Lee 2018, pp. 89–91.
- ^ Lee 2018, pp. 122–123.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 100.
- ^ Lee 2018, pp. 101–102.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 103.
- ^ Lee 2018, pp. 103–104.
- ^ a b c Lee 2018, p. 105.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 156.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 137.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 131.
- ^ do Carmo 1992, pp. 146–147.
- ^ Lee 2018, pp. 105–110.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 201.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 200.
- ^ Lee 2018, pp. 196–197.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 210.
- ^ Lee 2018, p. 207.
- ^ Burtscher 2015, pp. 275–276.
- ^ Burtscher 2015, p. 276.
- ^ a b Magnani & Tiberio 2020.
- ^ Michor & Mumford 2005.
Sources
- Lee, John M. (2018). Introduction to Riemannian Manifolds. Springer-Verlag. ISBN 978-3-319-91754-2.
- do Carmo, Manfredo (1992). Riemannian geometry. Basel: Birkhäuser. ISBN 978-0-8176-3490-2.
- Gromov, Misha (1999). Metric structures for Riemannian and non-Riemannian spaces (Based on the 1981 French original ed.). Birkhäuser Boston, Inc., Boston, MA. ISBN 0-8176-3898-9.
- Burtscher, Annegret (2015). "Length structures on manifolds with continuous Riemannian metrics". New York Journal of Mathematics. 21: 273–296. ISSN 1076-9803.
- Magnani, Valentino; Tiberio, Daniele (2020). "A remark on vanishing geodesic distances in infinite dimensions". Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 148 (1): 3653–3656. arXiv:1910.06430. doi:10.1090/proc/14986. S2CID 204578276.
- Michor, Peter W.; Mumford, David (2005). "Vanishing geodesic distance on spaces of submanifolds and diffeomorphisms". Documenta Math. 10: 217–245. arXiv:math/0409303. doi:10.4171/dm/187. S2CID 69260.
External links
- L.A. Sidorov (2001) [1994], "Riemannian metric", Encyclopedia of Mathematics, EMS Press
- v
- t
- e
- Topological manifold
- Atlas
- Differentiable/Smooth manifold
- Submanifold
- Riemannian manifold
- Smooth map
- Submersion
- Pushforward
- Tangent space
- Differential form
- Vector field
- Curve
- Diffeomorphism
- Geodesic
- Exponential map
- in Lie theory
- Foliation
- Immersion
- Integral curve
- Lie derivative
- Section
- Submersion
manifolds
| Vectors |
|
|---|---|
| Covectors | |
| Bundles | |
| Connections |
|






































































































![{\displaystyle {\begin{aligned}g_{p}(au+bw,v)&=\sum _{\alpha \in A}\tau _{\alpha }(p)\cdot ({\tilde {g}}_{\alpha })_{p}(au+bw,v)\\[5pt]&=a\sum _{\alpha \in A}\tau _{\alpha }(p)\cdot ({\tilde {g}}_{\alpha })_{p}(u,v)+b\sum _{\alpha \in A}\tau _{\alpha }(p)\cdot ({\tilde {g}}_{\alpha })_{p}(w,v)\\[5pt]&=ag_{p}(u,v)+bg_{p}(w,v).\end{aligned}}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/85c1cf22cb7a5b8bdcfce14f4c466da7980497de)








![{\displaystyle \gamma :[0,1]\to M}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/0066953642fb00abb394327531cea098815cd1c8)


![{\displaystyle [0,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/738f7d23bb2d9642bab520020873cccbef49768d)






















![{\displaystyle [0,\delta ].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/9d2de11de6feb4841f7d0c9fff9241a77e33a258)

















![{\displaystyle \nabla _{X}Y-\nabla _{Y}X=[X,Y],}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2ca63c0cb31ba4d14004adb8d8ec84cced774a8e)
![{\displaystyle [\cdot ,\cdot ]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/28dd4c22d60192519c1c12cf645b040f368db9e9)
![{\displaystyle X:[0,1]\to TM}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/11fcfd3cec8c7149af97f02bf8b630cee7d0dee8)

![{\displaystyle t\in [0,1]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/31a5c18739ff04858eecc8fec2f53912c348e0e5)

![{\displaystyle f:[0,1]\to \mathbb {R} }](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/2de6d0d4c98d4ca7ad937c772dc3e3e914b062f5)


































![{\displaystyle R(X,Y)Z=\nabla _{X}\nabla _{Y}Z-\nabla _{Y}\nabla _{X}Z-\nabla _{[X,Y]}Z}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6a30a969d5b599e29c8ef7fc0344b823845e5865)
![{\displaystyle [X,Y]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/94470b44d283fde62130212956058ca6b727da37)



































